Chapter 7. Safety of Flight
.Download link from urldecrypt, direct link under maintenance. File name: cue-vm-k9.aim.7.4.1.zip Upload Date: 2014-12-06T18:11:42.000Z Size: 115061593. ContentcopyThis file is hosted at free file sharing service 4shared. Aim at an imaginary ball is difficult. Parallel Aim, used by greats including Greenleaf, Mosconi, and Varner, uses real balls and adds imaginary lines. Visualize parallel lines to both contact points. Add lines connecting the points and parallel through cue ball center. Visualize lines that cross the ball equators and don't sight down on the cloth. Cue is an incredibly clever robot with a witty attitude that’s full of interactive surprises! Choose from four unique avatars to customize cue with a personality that’s right for you. The more you explore, the more you’ll discover what Cue can do. Cue Installer Aim 7.4.1 9/24/2019 I try to upgrade AIM-CUE with 1GB Flash i buy it from eBay the software include 2.1 i try to upgrade it to 7.4.1 but when i make software install clean.
Section 1. Meteorology
- 7-1-1. National Weather Service Aviation Products
- 7-1-2. FAA Weather Services
- 7-1-3. Use of Aviation Weather Products
- 7-1-4. Preflight Briefing
- 7-1-5. En Route Flight Advisory Service (EFAS)
- 7-1-6. Inflight Aviation Weather Advisories
- 7-1-7. Categorical Outlooks
- 7-1-8. Telephone Information Briefing Service (TIBS)
- 7-1-9. Transcribed Weather Broadcast (TWEB)
- 7-1-10. Inflight Weather Broadcasts
- 7-1-11. Flight Information Services (FIS)
- 7-1-12. Weather Observing Programs
- 7-1-13. Weather Radar Services
- 7-1-14. ATC Inflight Weather Avoidance Assistance
- 7-1-15. Runway Visual Range (RVR)
- 7-1-16. Reporting of Cloud Heights
- 7-1-17. Reporting Prevailing Visibility
- 7-1-18. Estimating Intensity of Rain and Ice Pellets
- 7-1-19. Estimating Intensity of Snow or Drizzle (Based on Visibility)
- 7-1-20. Pilot Weather Reports (PIREPs)
- 7-1-21. PIREPs Relating to Airframe Icing
- 7-1-22. Definitions of Inflight Icing Terms
- 7-1-23. PIREPs Relating to Turbulence
- 7-1-24. Wind Shear PIREPs
- 7-1-25. Clear Air Turbulence (CAT) PIREPs
- 7-1-26. Microbursts
- 7-1-27. PIREPs Relating to Volcanic Ash Activity
- 7-1-28. Thunderstorms
- 7-1-29. Thunderstorm Flying
- 7-1-30. Key to Aerodrome Forecast (TAF) and Aviation Routine Weather Report (METAR)
- 7-1-31. International Civil Aviation Organization (ICAO) Weather Formats
Section 2. Altimeter Setting Procedures
- 7-2-1. General
- 7-2-2. Procedures
- 7-2-3. Altimeter Errors
- 7-2-4. High Barometric Pressure
- 7-2-5. Low Barometric Pressure
Section 3. Wake Turbulence
- 7-3-1. General
- 7-3-2. Vortex Generation
- 7-3-3. Vortex Strength
- 7-3-4. Vortex Behavior
- 7-3-5. Operations Problem Areas
- 7-3-6. Vortex Avoidance Procedures
- 7-3-7. Helicopters
- 7-3-8. Pilot Responsibility
- 7-3-9. Air Traffic Wake Turbulence Separations
Section 4. Bird Hazards and Flight Over National Refuges, Parks, and Forests
- 7-4-1. Migratory Bird Activity
- 7-4-2. Reducing Bird Strike Risks
- 7-4-3. Reporting Bird Strikes
- 7-4-4. Reporting Bird and Other Wildlife Activities
- 7-4-5. Pilot Advisories on Bird and Other Wildlife Hazards
- 7-4-6. Flights Over Charted U.S. Wildlife Refuges, Parks, and Forest Service Areas
Section 5. Potential Flight Hazards
- 7-5-1. Accident Cause Factors
- 7-5-2. VFR in Congested Areas
- 7-5-3. Obstructions to Flight
- 7-5-4. Avoid Flight Beneath Unmanned Balloons
- 7-5-5. Unmanned Aircraft Systems
- 7-5-6. Mountain Flying
- 7-5-7. Use of Runway Half-way Signs at Unimproved Airports
- 7-5-8. Seaplane Safety
- 7-5-9. Flight Operations in Volcanic Ash
- 7-5-10. Emergency Airborne Inspection of Other Aircraft
- 7-5-11. Precipitation Static
- 7-5-12. Light Amplification by Stimulated Emission of Radiation (Laser) Operations and Reporting Illumination of Aircraft
- 7-5-13. Flying in Flat Light and White Out Conditions
- 7-5-14. Operations in Ground Icing Conditions
- 7-5-15. Avoid Flight in the Vicinity of Thermal Plumes (Smoke Stacks and Cooling Towers)
Section 6. Safety, Accident, and Hazard Reports
- 7-6-1. Aviation Safety Reporting Program
- 7-6-2. Aircraft Accident and Incident Reporting
- 7-6-3. Near Midair Collision Reporting
- 7-6-4. Unidentified Flying Object (UFO) Reports
| Aeronautical Information Manual (AIM) |
|---|
| Chapter 1 - Chapter 2 - Chapter 3 - Chapter 4 - Chapter 5 - Chapter 6 - Chapter 7 - Chapter 8 - Chapter 9 - Chapter 10 |
Today I went through Cisco unity express (CUE) loading, installation and configuration. Got a bit stuck in some to points, but successfully cross over those.
CUE files loading to a router/module is different form IOS and CME loading and installation.
First up all we require a module in router to load CUE files and mail boxes. That might be NME-CUE, NM-CUE, NM-CUE-EC, AIM-CUE, AIM2-CUE, ISE CUE, ISM-SRE-300-K9, SM-SRE-700-K9 and SM-SRE-900-K9. I my lab I used AIM-CUE. So the article based up on AIM-CUE…
So I am going to make this process in three parts:-
- Part 1 – Loading CUE files to Module
- Part2 – Configure CUE
- Part3 – GUI mode
Part 1 require when you have a physical lab with you and want to load the same. If you are using remote lab or taking CCIE lab exam, you can find all the files already uploaded in router.
Part1:-
Step1:- We need CUE files, hear I am using CUE version 7.0.6. As usual login to Cisco with CCO credentials and downloaded the files. I will suggest, don’t confuse about any think; go and download “Unity Express Complete Installation File Set” plus “Unity Express Language Packages” and “Unity Express License Packages”.
Note: Read the description carefully and select appropriate file which suite your module

Step2:- Unzip the entire file to FTP folder.
Note:As I early mentioned it’s not like IOS & CME loading. We need to use FTP server not TFTP. I used FileZilla Server (http://filezilla-project.org/download.php?type=server ). And it’s shareware…
Note an Error: – Hear I stuck, when I tried to install (the command below mentioned) got an error, access denied or authentication failed…
Because, TFP request always searching for a username & password, and Cisco send anonymousas username and password. So we need to create a username (anonymous) and password (anonymous) in FTP server side.
Step3:use “show ip interface brief” to find the module port. And In my lab it’s Service-Engine0/1
Step4:from “enable mode” use “service-module service-Engine 0/1 session” to login to the module.
“Offline” This command will take you offline mode and hear you give offline commands…
“Restore factory default” commands initiate factory reset mode and reboot. Module is using Linux kernel to operate.
Once reboot complete it will ask
do you wish to start configuration now (y,n)?
In normal scenario with router will give “no” but here we should give “yes” it’s mandatory. Once reload complete, will configure admin username and password which use to login CUE GUI mode
Step5: Now we are going ahead with CUE installation, use the below command to accordingly
Software install clean url ftp://<IP>/cue-vm-k9.nm-aim.7.0.6.pkg
Note an Error: – I got an error code 550 : error type ‘Can not find package file’, And its noting but my FTP server folder doesn’t contain all the package file which is required to install CUE.
Once installation complete, It will reboot and again ask “to do you wish to start configuration now (y,n)?” give yes and follow the steps as earlier.
Step6: Now will install license for the mail boxes with the below command
Software install clean url ftp://<IP>/cue-vm-license_50mbx_cme_7.0.6.pkg
Yes guessed right, we done with the installation of CUE…
Note:- If you want get exit from CUE module simply type “exit”. This will work like a clean termination of connection form module to router.
If you want to move form module to router witout droping the process use key brake code, it’s the same what we are using in access switch, router. But a small change..
in access switch and router we are using – Ctrl+Shift+6 then press X
In module use – Ctrl+Shift+6 again Ctrl+Shift+6 then press X
Part2:-
Before moving ahead with Part2, need to go through Part1 step4. It’s not a mandatory step…. but help you to make sure the initial configuration view or can use sh run in module interface.
Step1: Hear we create a bridge between the module and router so that the router will communicate with Module.
interface Service-Engine0/1
ip unnumbered Loopback0
service-module ip address 177.1.254.4 255.255.255.0
service-module ip default-gateway 177.1.254.3
Give a “no shut” to active the port.
ip unnumbered Loopback0 – loopback address to bind
service-module ip address – will give ip address to the module and this ip will use to access the CUE in GUI mode
service-module ip default-gateway – is pointg to the loobback address configured in router
Step2: enable ip route to sent traffic to AIM-CUE
ip route <ip of module> 255.255.255.255 Service-Engine0/1
Step3: Configure this router as http server and path to gui file
ip http server
ip http authentication local
ip http path flash:gui
Step4: create a dial-peer to mail box
dial-peer voice 6000 voip
destination-pattern 6600
session protocol sipv2
session target ipv4:177.1.254.4
dtmf-relay sip-notify
codec g711ulaw
no vad
Step6: Some time the callerid sedning may mor ethan 4 digits, which is going to be missmatch with the abovr dial-peer.
So need to be strip for that we create a translation rule and create a profile which put in to the dial-peer.
Creating a translation rule
voice translation-rule 6000
rule 1 /.*(…./)/ /1/
Creating a Profile
voice translation-profile vm
translation calling 6000
Assign the profile to a dial-peer
dial-peer voice 6000 voip
translation-profile outgoing vm
Step5: Create ephone-dn for MWI on and off
ephone-dn 3
number 8001….
mwi on
!
ephone-dn 4
number 8000….
mwi off
Step6: in “telephony-service” configure call forward, credentials and edit privilege to CUE.
telephony-service
voicemail 6600
web admin system name <voicemail> secret 0 <cisco>
dn-webedit
Cue Installer Aim 7.4.1 Login
time-webedit
Step7: configure ephone-dn with forward busy and timeout (This is an optional, coz this configs will download forn GUI…. if you configure there.. )
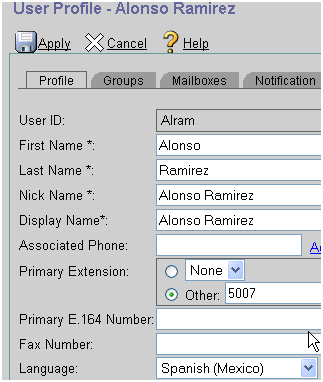
ephone-dn 1 dual-line
Cue Installer Aim 7.4.1 Version
number <extension>
call-forward busy 6600
call-forward noan 6600 timeout 10
Step8: configure ephone for usename and password. Without this CUE GUI will not detect the phone.
ephone 1

device-security-mode none
mac-address <0009.E881.2CE5>
username phone1 password 1234
button 1:1
Cue Installer Aim 7.4.1 2017
Part3:-
Now we can access the CUE GUI, using web browser by the IP address of service-module ip address (Mentioned above). And no need to use https://, just type the IP and give enter…
Will get page like below; were you need to give the username and password, which configured @ GUI installation stage.
If you are login in to CUE first time, next page you need to give jtapi username and password, which we configured in telephony-service mode:-
Web admin system name voicemail secret 0 cisco
That’s it we done the installation of CUE with basic configurations…
Cheers,
An